Medial Branch Nerve Blocks
![]()
Call (703) 520-1031 or use the form below to send us your contacts.
People with back or neck pain frequently see a physician asking for relief. One of the possible treatments is the medial branch nerve block, a minimally invasive procedure that is used for diagnostic purposes to identify the specific spine facet joints where the pain is originating. If the procedure works, the nerve branch block provides temporary therapeutic pain relief.
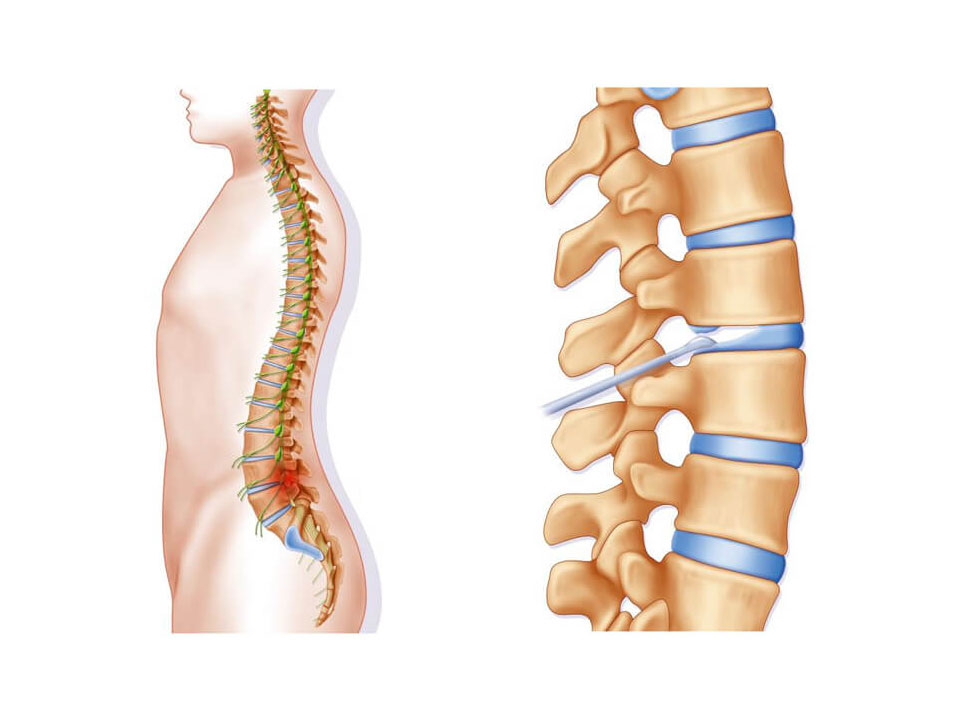
What is a Medial Branch Block?
Medial branch nerves are found just outside facet joints. Facet joints are the small, bony joints connecting spine vertebra. The spinal nerve root runs through facet joints and webs out from there. The dorsal ramus nerve is the first sub-divided nerve running out of the major spinal nerve root. In further nerve distribution, the medial nerve is one of three nerve branches coming out of the dorsal ramus.
The medial branch nerves mostly contribute to the operation of back muscles and facet joints. The facet joints give the spine its flexibility, so people can twist and bend within limits. The medial branch nerves transmit pain signals to the brain when the nerves are inflamed, pinched or experiencing some other issue.
How is the Medial Branch Block Procedure Performed?
Back or neck pain can be relentless and debilitating, driving people to see a physician for help. The medial branch blocks are medical procedures initially used for diagnostic purposes to help pinpoint the source of the pain. It can be used at any point along the spine.
The medial branch nerve block procedure involves the following steps:
- The patient lies on the stomach on a table in an x-ray room that has fluoroscopy equipment
- The patient and physician will decide if intravenous or oral sedation is necessary
- The skin where a needle will be inserted is cleaned with an antiseptic and then numbed with an anesthetic
- Using fluoroscopy for guidance, a needle is directed to reach a place over the medial branch nerves
- A small amount of anesthetic is injected into each targeted nerve
- The patient rests in a recovery room for 30 minutes
- The physician then assesses how the patient is feeling
What is the difference between a facet joint injection and a medial branch nerve block?
Facet joint injections involve injecting a steroid into the joint. The medial branch blocks injections place the anesthetic over the nerves.
Median branch nerve blocks (medial is sometimes misspelled when people are searching for pain relief) are frequently used as diagnostic procedures to identify the source of pain. It is not always easy to figure out which nerves are sending the pain signals unless there is an obvious spinal problem, like nerves placed under pressure due to spinal stenosis. As a diagnostic procedure, it may take more than one nerve block procedure to pinpoint the source of pain.
In many cases, the medial branch nerve block does relieve pain for a period of time. In that case, further treatments become therapeutic, meaning they are pain treatments.
Common and Uncommon Side Effects
There is always the possibility patients will experience side effects of any medical procedure. The medial branch block side effects are usually minimal, but it is important to be aware of all possibilities. They include:
- Dizziness
- Allergic reaction (usually due to the dye or anesthetic)
- General weakness
- Weakness in the legs
- Difficulty walking
- Drowsiness for 24 hours
- Bleeding
- Hiccups
- Fever
- Infection
- Worsening of pain
- Nerve injury
Some people experience side effects from the anesthetic medication. They include headache, muscle cramping, nausea, and flushing. A caution is that people with glaucoma or congestive heart failure need to be alert to physical changes, like fluid retention or blurred vision. Developing a fever within three days of the procedure is another possible side effect that should be reported to the physician.
The side effects last from a few hours to several days for most people. The injection sites may remain sore sometimes for up to three weeks.
Benefits
The goal of the medial branch nerve block is to stop the pain for a period of time. If the procedure is successful, the pain after medial branch block should subside over the following days. A successful procedure can lead to the patient feeling partial or complete pain relief within six hours. By 30 days, the maximum pain relief is reached.
How long does a medial branch block last? The usual pain relief period is anywhere from 6-14 months. Having said that, some patients get relief for less than six months or get little or no relief. When pain is not significantly improved by 30 days after a diagnostic medial branch block, the procedure will likely be repeated to target different nerves.
If it is successful, the procedure targeted the correct nerves causing the pain and could be repeated when the pain returns. When the physician is certain the procedure worked, radiofrequency ablation is an option. This procedure creates a heat lesion on the nerve to serve as a longer pain signal block.
If the nerves targeted were not the ones causing the pain, the medial branch nerve block will not relieve pain. All first-time medial branch nerve block procedures are diagnostic and all procedures repeated to pinpoint the facet joints that are the source of pain are diagnostic. If the pain goes away and stays away, the block is used for therapeutic purposes.
Managing Pain
There are many ways to address back or neck pain. The medial branch nerve block is one way and is frequently successful. If back or neck pain is disrupting life, consult a spine specialist to discuss medical procedure options.