Table of Contents
- Impact of Osteoarthritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Physical Therapy in Treatment Plans
- Types of Physical Therapy
- Individualized Treatment Plans
- For All People with Arthritis
Joints are designed to be used regularly, but it is tempting to become inactive when arthritis causes joint pain. It is one of the worst things to do, but many people do not know how to start an exercise program specifically for joints experiencing arthritis. They need guidance, which is one of the benefits of physical therapy. What does physical therapy help with? It helps people with arthritis reduce pain and increase mobility and balance, just a few benefits.
Reducing the Impacts of Osteoarthritis and Rheumatoid Arthritis
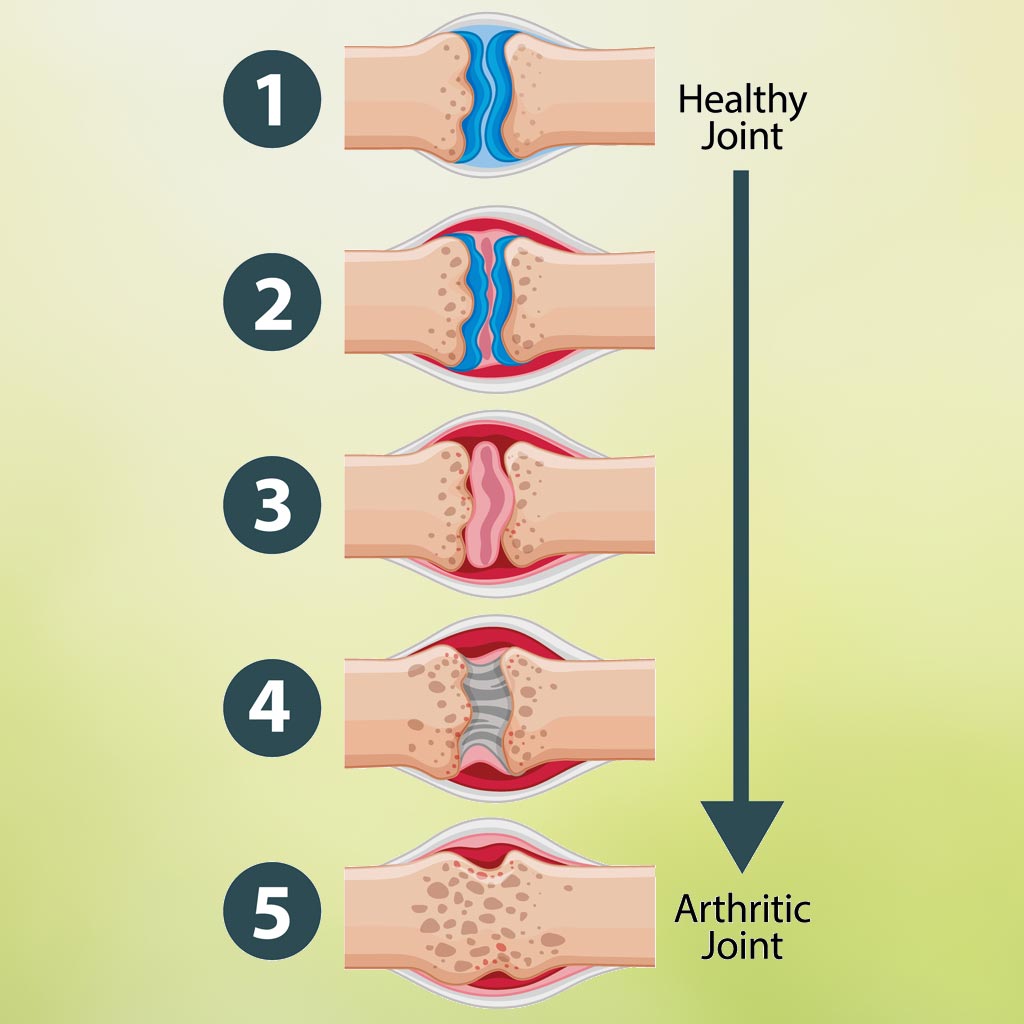
Osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis have different causes. Osteoarthritis is a joint wear-and-tear disease, while rheumatoid arthritis is an autoimmune disease in which the body’s immune system attacks tissues. Some people have both. Despite the different causes, the two types of arthritis have a lot in common.
Each type of arthritis can cause swollen and painful joints, joint inflammation, reduced joint flexibility, balance issues, joint weakness and joint stiffness. It is tempting to avoid using painful joints, but that is likely to make the symptoms worse. The impact on the quality of life is measurable, so a physician will often include physical therapy in an arthritis treatment plan.
Why Physical Therapy is Included in Treatment Plans
Physical therapy as a treatment for arthritis has been the subject of many clinical studies. It is a preferred treatment because it is conservative, non-invasive and effective. Does physical therapy help arthritis? The answer is yes, it does.
The goal of physical therapy is to:
- Relieve arthritis symptoms
- Improve joint function
- Slow down the progression of the disease
- Increase joint strength, mobility and flexibility, which reduces the degree of potential disability
A core element of any physical therapy program is exercise. The physical therapist delivers exercise therapy and can provide education on managing arthritis with exercises at home. Does physical therapy help osteoarthritis? Physical therapy not only helps but is also recommended as a first-line treatment for osteoarthritis.
Exercise therapy has been found to provide as much pain relief as pain medications without the risk of adverse effects. Physical therapy has also been found to be effective for people experiencing different levels of pain intensity and severity.
Types of Physical Therapy
The physical therapist can incorporate different types of exercise and other strategies in the treatment plan. All treatment plans have exercises that focus on increasing joint range of motion.
1. Manipulation Exercises
The stretching, rolling and flexing joint exercises lubricate the joints and reduce joint stiffness.
2. Strengthening Exercises
Exercises that strengthen the muscles, tendons, and ligaments supporting the joints are also included in the treatment plan. This reduces the stress your body is placing on the joints and increases the joints’ ability to accommodate different movements.
3. Hydrotherapy Exercises
The physical therapist may have an exercise pool where water therapy exercises are performed. Doing exercises in water relieves some of the body’s weight on the joints.
4. Isometric exercises
These are static exercises that have a low impact. These exercises require tightening muscles without moving the joints. They have been shown to significantly impact the range of motion, pain intensity, and functional ability in patients with knee osteoarthritis in a positive way.
The physical therapist may supplement exercises with additional interventions. For example, Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) reduces pain. The 2019 American College of Rheumatology guidelines strongly recommended using TENS for osteoarthritis pain. Though the effects are short-term, reducing pain can help you perform exercises better during physical therapy sessions and at home.
Exercise therapy improves joint symptoms, strengthens other muscles, like the back and abdomen muscles involved in posture, and complements weight management programs.
A common question is, “Can physical therapy make arthritis worse?”
The exercises will not make arthritis worse. The physical therapist is trained to avoid joint injury. However, you may find some of the exercises challenging in the beginning. The exercises should not lead to worse arthritis symptoms. Not exercising will make arthritis worse.
Individualized Treatment Plans
The physical therapist develops an individualized treatment plan for each patient. In addition to the exercises completed with the physical therapist, you will learn how to do exercises at home properly. Other information the therapist shares includes:
- Learning how to use assistive devices to best assist joints with minimum risk
- Developing good posture to reduce joint stress and pain
- Learning body mechanics that improve the ability to manage daily activities
- Suggesting accessories that can relieve joint pain and stiffness, like shoe inserts and braces
- Making recommendations about things like ergonomic chairs, mattress support, etc.
You will learn to use hot and cold compress therapy to reduce joint inflammation and pain. If you are overweight, your doctor and physical therapist will discuss strategies for losing and maintaining a weight that avoids placing extra stress on joints, especially the weight-bearing joints.

For All People with Arthritis
Many people find that with a treatment plan that includes PT, joint pain and stiffness are much more manageable. Though physical therapy is often associated with osteoarthritis, it is just as crucial for people with rheumatoid arthritis. A review of 13 study databases found that only exercise and physical activity interventions were most effective in reducing the range of impacts related to rheumatoid arthritis.
One of the many advantages of utilizing the services of a physical therapist is that the exercises can be modified or the treatment plan revised as your needs change. Your pain doctor at SAPNA pain clinic will collaborate with the physical therapist to ensure you get the best care possible.
![]()
Call (703) 520-1031 or use the form below to ask any questions concerning physical therapy and arthritis treatment.
Sources
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8104171/
- https://www.clinexprheumatol.org/abstract.asp?a=14740
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8604435/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9611192/
- https://www.arthritis.org/health-wellness/treatment/complementary-therapies/physical-therapies/physical-therapy-for-arthritis
- https://journals.lww.com/jbisrir/Abstract/2019/07000/Effectiveness_of_non_pharmacological_and.15.aspx
