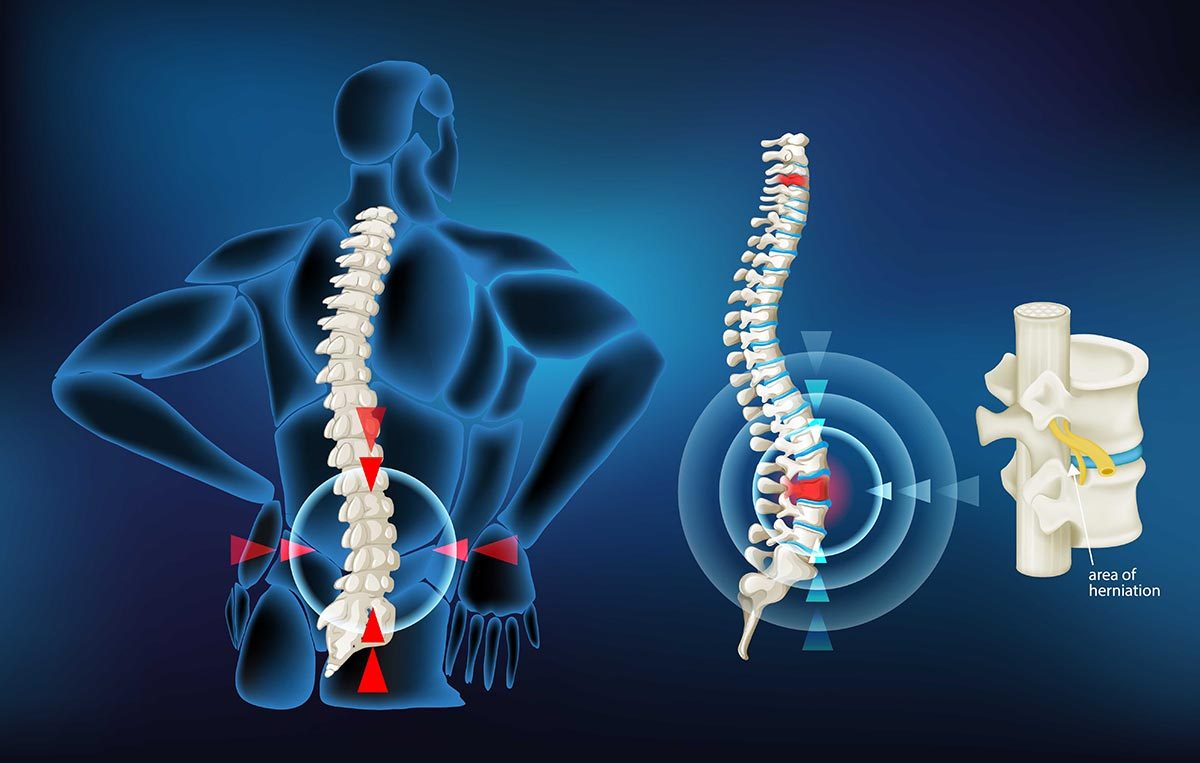
Herniated Disk
![]()
Call (703) 520-1031 or use the form to send us your contacts.
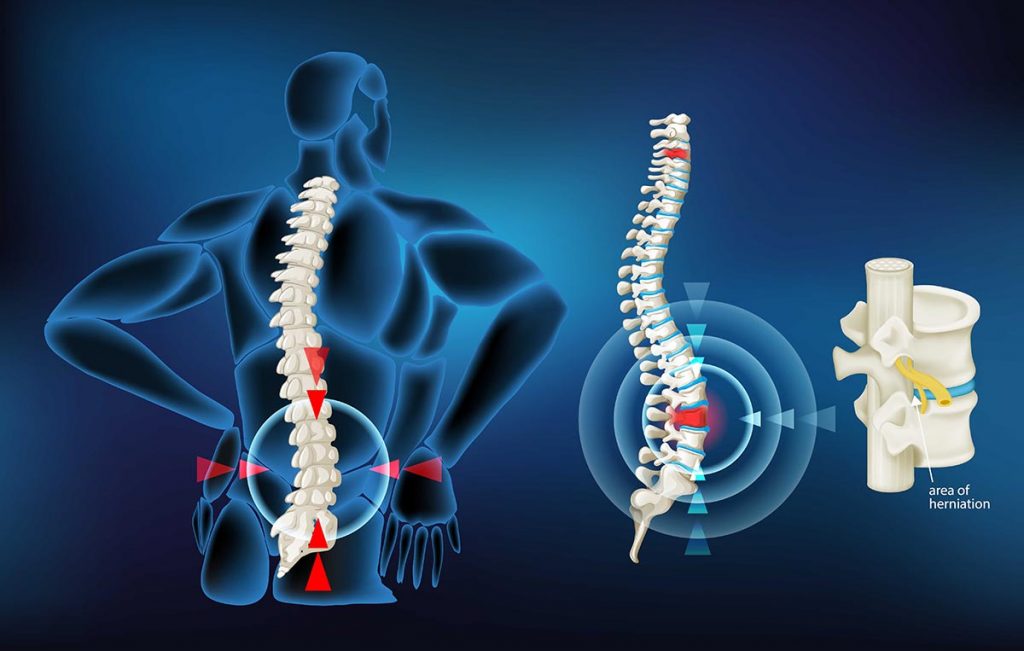
What is a Herniated Disk?
A herniated disc is a condition that affects the back. It can cause pain, numbness, or tingling down one or both legs. It refers to a problem with intervertebral disks (the rubbery cushions between the individual vertebrae that stack up to make a spine).
An intervertebral disk is a small jelly-like donut, with a softer center (nucleus pulposus) encased within a tougher outer fibrous ring. A herniated disk occurs when some of the softer nucleus pulposus pushes out through a tear in an outer fibrous ring. A herniated disk can irritate or compress nearby nerves and lead to pain, numbness or weakness in an arm or leg. Nevertheless, many people have no symptoms of a herniated disk and do not need surgery to repair the disk.
Causes of Herniated Disk
Disk herniation is usually caused by a gradual, aging-related wear and tear called disk degeneration. Also, spinal disk’s tissues lose some water content with aging. Therefore, they become less flexible and more predisposed to tearing or rupturing.
Factors that increase the risk of disk herniation may include:
- Excess body weight can cause extra pressure on the disks.
- Physically demanding jobs. Repetitive lifting, pushing, bending sideways and twisting may increase the risk of a herniated disk.
- Predisposition to developing a herniated disk can be inherited.
Symptoms
The most common symptoms of a herniated disk are:
Arm or leg pain. If the herniated disk occurs in the lower back, you will typically feel the intense pain in buttocks, thigh, and calf. The foot can also be involved. If the herniated disk is in the neck, the pain will typically be most intense in the shoulder and arm.
Numbness or tingling. Patients with a herniated disk often feel numbness or tingling in the body region served by the affected nerves.
Weakness. Muscles served by the affected nerves tend to weaken.
Treatments
A small number of people end up needing surgery to treat a herniated disc. However, most patients do well with simpler treatments, such as:
- Pain medicines.
- Drugs originally designed to control seizures may also be helpful in the treatment of the radiating nerve pain associated with a herniated disk.
- Cortisone injections. Inflammation-suppressing corticosteroids may be given by injection directly into the area around the spinal nerves.
- Medicines to relax the muscles (called muscle relaxants).
- Injections of medicines that numb the back or reduce swelling.
- Physical therapy teaches you special exercises and stretches.
In some cases, people with herniated disks need surgery. Your physician can suggest this when conservative treatments fail to reduce pain after six weeks. Moreover, surgery is indicated for patients who continue to experience:
- Numbness or weakness
- Difficulty standing or walking
- Loss of bladder or bowel control
In most cases, surgeons can remove just the protruding portion of the disk. However, in some cases, the entire disk must be removed and after that, the vertebrae may need to be fused together with metal hardware.
Herniated Disk FAQ
How long does it take to recover from a herniated disc?
The pain associated with a herniated disc will normally improve within 4-6 weeks of treatment. Most herniated discs heal on their own with persistent conservative treatment, like applying heat to your back and doing stretching exercises to reduce muscle tension.
Is a herniated disc permanent?
In most cases, the herniated disc is not permanent and does not cause permanent damage to the spine or nerves. However, if pain persists for a week or more, it is important to see a doctor for an assessment.
Can you be paralyzed by a herniated disc?
In the worst cases, a herniated disc can lead to paralysis of one or a group of muscles. However, this is very rare.
Is a herniated disc serious?
Though many herniated discs heal on their own, they can become a serious medical problem. A herniated disc can cause permanent nerve damage and even lead to loss of bladder or bowel control. If the pain of a herniated disc does not improve after home treatment within a week or serious complications occur, it is important to see a doctor right away. The sooner the herniated disc is treated, the less likely serious complications will develop.
How painful is a herniated disc?
When the herniated disc is located in the lower back, the pain usually radiates into the buttocks and down the leg. When the herniated disc is in the neck, the pain radiates into the shoulder and down the arm. It is frequently described as a burning or sharp pain.